Internet Safety For Kids? What does that really mean?
Well, Children’s relationship with cyberspace has grown tighter. This comes true with the emergence of digital devices and global Networks. Being born in the age of digital interdependence, 7-year-old internet users are interested in the content dedicated to older users. This tendency can exert negative impacts on their behavioral and personal traits.
The following guide will provide you with the best internet safety tips to protect your child from any type of unsuitable online content.
-
What is the average time a child spends on the Internet?
A recent study has revealed that 80% of American children under the age of 5 surf the Internet at least once a week. In fact, the more a child grows old, the more time they spend online.
In addition, around 42% of children between 8 and 11 years old navigate the Internet more than once per day. As for teenagers, research has found that most of them surf the Internet daily. This phenomenon is common among South Korean teenagers as well, who are reported to have developed an addiction to cyber activities.
Nowadays it is easier to access the Internet. Whether at home or in coffee houses, children in developing countries can go online any time they wish, thanks to fixed Broadband Internet access.
According to recent research, the Asia Pacific region is ranked the first in mobile Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) usage, with about 980 million subscribed smartphones in India alone.
There are about 7 billion people in the world who access the Internet using their phones, 230 million of which use Mobile Broadband. Most Latin Americans use mobile broadband for its flexible nature made possible by the high network coverage in the country.

-
What are the most used Digital devices to access the Internet?
Laptops, desktops, phones, and tablets are among the gadgets that offer Internet accessibility. According to a 2014 study conducted in the UK, more than one-third of teenagers between 12 and 15 access the Internet via their mobile phones. As for tablets, their usage increased from 39% in 2013 to 54% in 2014.
Using the Internet was proven beneficial for children. Their smartphones offer them a wide range of services that can help them communicate with others in different areas and indulge in educative pursuits. These perks can be advantageous to all children, especially natural disasters nomads whose unstable life relies heavily on communicative networks.
-
Can the Internet be a good source of information?
Some children resort to the Internet while doing their homework. They consult online encyclopedias, such as Wikipedia, to figure out the correct answers to their assignments. A study has shown that this is mostly common among children between 8 and 11, forming 75% of the whole number of children, and teenagers between 12 and 15 being 84% of the age category.
Wikipedia ranks the first online encyclopedia consulted by minors. This free multilingual source contains modifiable articles about almost every required subject, with the perk of code-switching which shores up any linguistic gap. Study groups are also accessible for children who wish to seek help from their fellow students.
-
Can Social Networks enhance socializing skills?
For many children, signing up with a personal profile is the first step to intercultural exchange. Socializing over the Internet and bridging cultural gaps have become attainable with just one click.
Besides forming cross-cultural connections, nonsecure to social media for entertainment. In the UK, 1 in 4 children signs in to Twitter where they can share videos, pictures, and texts. YouTube, Snapchat, and Instagram are among the same category of online apps where children can enjoy multi-sensory media.
-
Why is it important to preserve Internet Safety for kids?
Children are constantly prone to encounter all forms of illicit content online. Whether embedded in games and posts or epitomized in pop-up ads, such offensive content can have acute impacts on the child’s mental, psychological, and behavioral development.
Given children’s curious nature, it would be hard for them to resist clicking on such pop-up ads or random links. Therefore, it is the parent’s responsibility to limit their exposure to obscenity.
-
Facts about children’s exposure to obscenity:
- More than 40% of children reported being exposed to nudity.
- 1 child per 16 has watched hardcore pornography.
- 1 child per 12 has exchanged sexual media over social networks.
- 1 child per 25 has had their private photos shared publicly.
- 25% of children access adult websites incognito or by faking their age to create an account.
- 1 child per 20 arranged real-life meetings with strangers on the Internet.
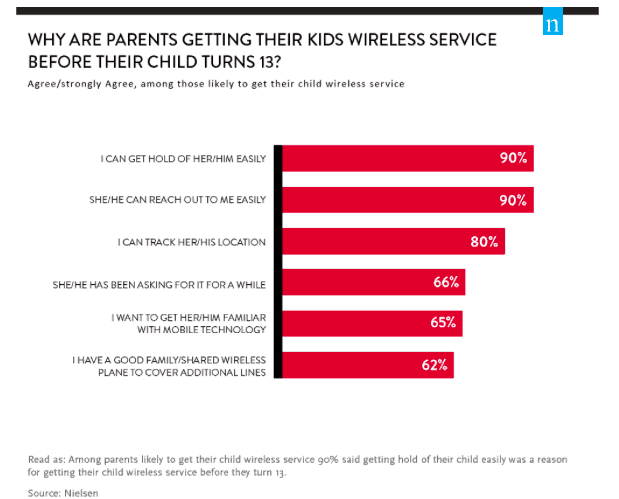
These statistics reveal the immense danger awaiting youngsters on social media. Being part of the digital-oriented generation, kids typically have their first smartphone between 10 and 13. The earlier they acquire their smartphone, the more their liability for damage increases, and the harder it becomes for parents to track their activity. Some parents even deny the offensive innuendos as they consider smartphones as no more than a communication tool.
- Children’s average wireless usage:
- The average age for a child to have their own mobile phone is 12
- About 53% of children own a cellphone at the age between 8 and 12
- About 69% of families grant their 8-year-old child a cellphone
- About 38% of children below 2 have used a smartphone to watch videos.
-
How to manage your child’s online activity?
Children’s curious nature makes them always eager to learn more from the Internet. Many educational, entertaining, and communicative activities are available in the online grid. However, hackers and identity thieves are always creeping around. These cyber criminals target your child’s confidential data to steal and abuse. Besides, the Internet cannot be a safe space due to all the cyberbullying and harassment.
For the aforementioned reasons, it is high time you started protecting your child online.
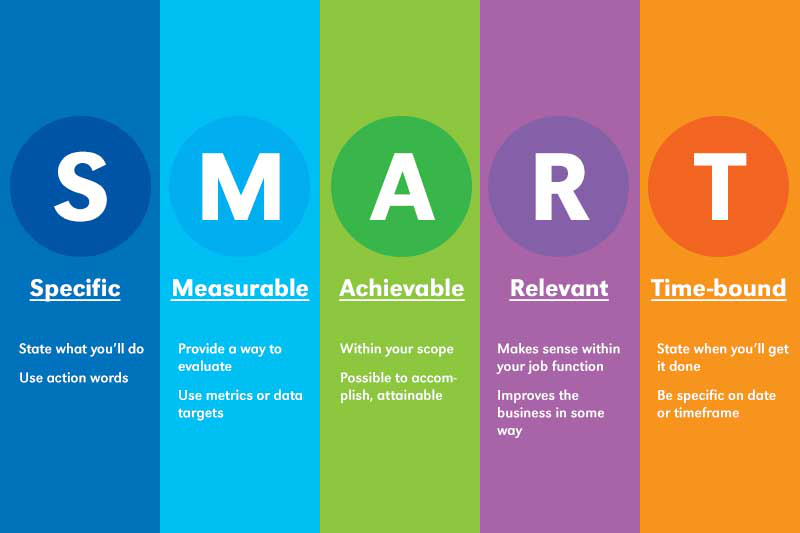
Abide by the S.M.A.R.T rules to protect your, kids, online:
-
S – Set Limits :
Some websites require you to posit your personal data before logging in. This can threaten your privacy as a user and enable cybercriminals to steal your identity or confidential information. It is better to access websites anonymously. Using an incognito tool like a VPN helps to conceal and protect your user identity.
-
M – Meeting Online :
Many real-life friendships start with a chat between strangers. It is highly recommended to have company when meeting an online friend in real life for the first time. Taking one of your parents with you would protect you from any undesired plot twists.
-
A – Accepting Invitations :
Social networks enable you to form many acquaintances in a short time. It is important not to quickly consider them as friends and open up to them about your private life.
-
R – React :
You need to develop a rational reflex against any illicit media. If you were exposed to an ad, a picture, a video, or a text with an offensive tendency, refer to your parents and communicate your feelings. Chat rooms can also be a source of distressful exchange. You are asked to immediately leave the conversation and block the user if this latter causes you any type of malaise.
-
Tell Someone:
If anything on the Internet causes you any sort of disconcertment, it is best to consult your parents or any reliable person from your circle. It is crucial to seek advice from a grown-up to avoid any reckless decisions that may lead to tremendous consequences. You can resort to the children’s free helpline in your country, as well. This resource acts as a supportive platform with a protective policy designed to solve child-related emergencies. For an immediate reaction, you can use the block and report options that come with almost every medium.
Additional internet safety tips (for parents)
- Be involved in your child’s online activity:
Parents should keep track of their child’s online activity. Supervise the links they access, the persons they indulge in conversations with, and the media they share with others. Interference might not be immediate, so make sure to communicate with your child about how they should autonomously react to inappropriate content.
- Teach your child how to act autonomously in inconvenient situations:
- Abide by the Internet use policy.
- Never share intimate media publicly.
- Never publicize your personal information, namely your address, location, identity details …etc.
- Use a unique username for identification and keep your password and login credentials private.
- Seek your parent’s approval before deciding to meet online acquaintances in real life.
- Use machines and digital devices safely
Make sure you are acquainted with the safe way to use your digital devices. Regularly update your anti-virus software. Understand your computer’s operating software. Check if it has an implemented parental control tool and use it to adjust your Internet content to your child’s age and preferences.
Do not crack parental control. Never click on random links from untrusted sources as they can be Trojan or viruses targeting your machine’s safety. Learn how to react rationally and quickly to protect your device.
-
Respect the Internet safety for kids policy:
The Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) is a United States federal law passed in 1998. It is designed to hinder any endeavor to abuse personal information from children under 13 by notifying their parents. COPPA enjoins websites to make their access to children’s personal information contingent upon parental consent. With the enactment of this public law, children are no longer compelled to share their private data before registering in contests or playing online games.
- Know your child’s rights and responsibilities:
- Every child has the right to use technologies to enhance their skills and mold their personality.
- Every child has the right to identity protection.
- Every child has the right to access online educational and entertaining content suitable for their age and preferences.
- Every child has the right to freedom of expression in a milieu characterized by mutual respect.
- Every child has the right to discuss any subject matter without being attacked or condemned for it.
- Every child has the right to SAY NO! To any potential disturbance.
To sustain your child’s cyber safety, it is highly recommended to go by the book! Abide by the security policy and follow the rules (mainly our internet safety tips) and always remember that safety is both your child’s right and responsibility.
At the end of this article, please provide us with your constructive feedback. Can you suggest new Internet Safety tips for kids that were not included in this article?
This article is for informational purposes only and is not meant to offer medical advice.

A Content Writer & Freelance Translator. He enjoys writing about mental health, fun for seniors, educational apps, and entertainment for all. In his spare time, he enjoys watching football, playing video Games, and good laugh with his friends.









